What's the difference between JDK, JRE and JVM?
What is JDK?
JDK stands for Java Development Kit. It consists of the JRE, JVM and development tools. JDK is a development kit used to create Java programs and applications, and convert them to the format that the JRE and JVM can execute.
It provides tools such as the
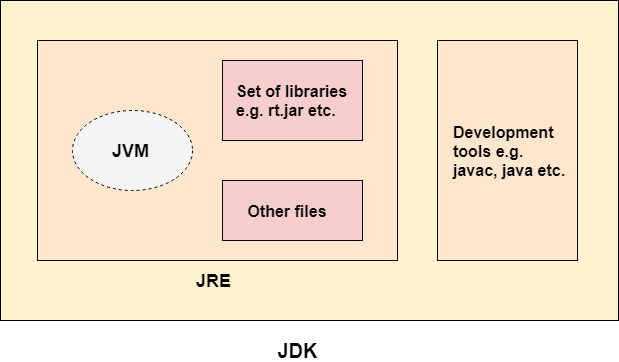
The JDK architecture
The JDK architecture is a collection of the JDK, JRE, and JVM. It combines the interpretation and compilation processes, outlining the steps involved in developing a Java program.
The JDK, together with the JVM and the JRE, is one of three key technology packages used in Java development. It’s critical to grasp the differences between these three technologies, as well as how they’re linked.
The JVM is the component of the Java platform that runs programs. It converts the byte code to machine specific code.
The JRE is the on disk component that generates the JVM. It contains the class libraries and other supporting files required by JVM to run the program.
The JDK allows programmers to construct Java applications that the JVM and JRE can execute and operate.
JDK Components
Javac
This is used to compile the source code into byte code.
Java
This is used to load the class files and interpret the source code compiled by the Javac.
JavaDoc
This is used to document details of the code.
Jar
The jar helps the archives to manage the jar files in the package library.
JConsole
This a Java management and monitoring unit.
Appletviewer
This is used to run and debug Java applets without an internet browser.
What is JRE
The JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. This platform is used to run and execute source code. It consists of the JVM and provides the libraries to execute the program. It integrates the the software plugins, jar files, and support libraries necessary for the source code to run.
Components of the JRE
JRE is composed of a variety of supporting software tools and features to run Java applications. These include the following.
Deployment solutions
Deployment technologies, like Java Web Start and Java Plugin, are included as part of JRE installation; they simplify the activation of applications and provide advanced support for future Java updates.
Toolkits for developers
The JRE includes toolkits to assist developers in the improvement of user interfaces.
Java 2D
An Application Programming Interface (API) that lets you draw two-dimensional graphics in the Java language.
AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
A graphical user interface (GUI) to create objects, buttons, scroll bars, and windows.
Swing
Another lightweight GUI that makes use of a large number of widgets to provide flexible, user-friendly customizations.
The Java Runtime Environment includes a number of integration libraries that can help developers create smooth data connections between their apps and services. Some of them are discussed below.
Java IDL (CORBA)
Supports distributed objects defined in the Java programming language with the Common Object Request Broker Architecture.
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) API
Provides developers with the tools they need to create applications that can access remote relational databases, flat files, and spreadsheets.
Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI)
A programming interface and directory service that allows customers to construct portable applications that use naming conventions to get data from databases.
Libraries for languages and utilities
The java.lang. and java.util. packages, which are essential for the design of Java programs, package versioning, management, and monitoring, are included with the JRE. Some of these packages include:
Collections Framework
The collections framework is a unified architecture made up of a collection of interfaces meant to improve the storage and processing of application data.
Concurrency Tools
A comprehensive framework that includes high-performance threading utilities.
Preferences API
A cross-platform, lightweight persistent API that allows several users on the same machine to create their own set of program preferences.
Logging
Generates log reports for further study, such as security failures, configuration errors, and performance concerns.
Java Archive (JAR)
A platform-agnostic file format that allows many files to be bundled into a single JAR file, which significantly improves download speed and reduces file size.
What is JVM
JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine, and it provides the run time environment for code execution. It runs on any machine and translates the byte code to the native code of the machine. The write once, run everywhere feature of the Java programming language is possible because of the Java Virtual Machine.
JVM Components
1. ClassLoader
It is used to load the class files.
2. Method Area
It stores class structures like metadata, method pool etc.
3. Heap
All objects and their related instance variables are stored in the heap.
4. PC Registers
The Program Counter(PC) stores the address of the Java virtual machine instruction, which currently executes in Java.
5. Execution engine
It is the central component of the Java Virtual Machine.