What is the #line directive in C?
The #line directive is one of the widely used directives in C. Its main purpose is to reset the line number and filename in the code. This means that we can reset any line of code to an arbitrary line number or a filename defined by the user.
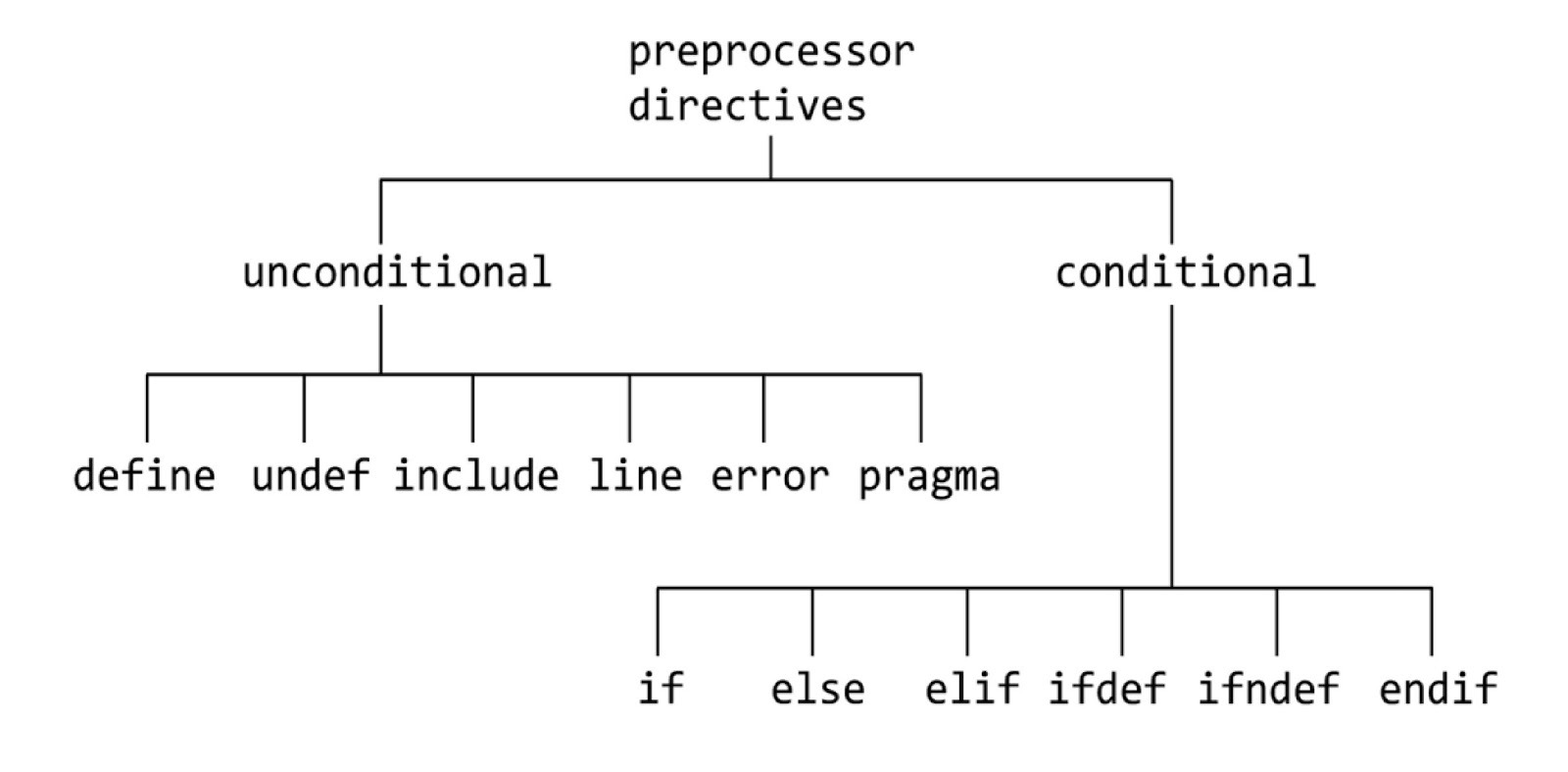
#line is an unconditional preprocessor directive
Syntax
#line <new line number> <new file name>
Code
Let’s look at a code example for the use of #line.
#include <stdio.h>int main(){printf("Hello world\n"); // this is line 6printf("Line: %d\n",__LINE__); // printing line number, line 7#line 23 //reseting to 23, although next line number is line 10.printf("Line: %d\n",__LINE__); // printing line numberprintf("Line: %d\n",__LINE__);printf("Line: %d\n",__LINE__);// let's try with filename (main.c) as well.printf( "Line: %d, File: %s\n", __LINE__, __FILE__ );// now we use line to reset filename to "new_filename.c"// line number is set to 83#line 83 "new_filename.c"printf( "Line: %d, File: %s\n", __LINE__, __FILE__ );return 0;}
Free Resources
Copyright ©2025 Educative, Inc. All rights reserved