What are HTML5 semantics?
Semantic elements are popularly used in HTML5. Semantic elements are simply HTML tags whose names indicate the kind of content they display on web pages.
At the advent of the internet, web pages were especially used to display scientific documents, but as internet usage grew, there was a pressing need to display web content in a more consistent layout.
Web programmers found a way around displaying content meaningfully and had a bunch of tags at their disposal. These tags are called structural tags and are largely used for laying out web pages. With the recent changes made to the HTML4 specification, HTML5 was introduced with an improved syntax for laying out web pages. This is known as semantic markup.
Semantic vs. non-semantic markup
<header></header>
<main>
<section>
<article></article>
</section>
<aside></aside>
</main>
<footer></footer>
The markup above shows how semantic markup can be used to section content on a web page.
The <header> element
The <header> element is usually found at the beginning of an HTML document. <header> normally contains the main heading and some navigation tools.
The <nav> element
The <nav> element is used to group menu items into a navigation section.
The <section> element
The <section> element is mostly used to group content with a similar scope on a page. For instance, the furniture section in an interior design page. <section> is sometimes confused with the <article> markup.
A collection of <article> tags can be placed in a section. This is intended to provide highlights to the section scope. For instance, the different types of chairs and tables can be discussed under the article section.
These tags are very suitable for laying out blog posts and news websites.
The <aside> element
The <aside> element is used to display content that is not part of the flow of the document but is related to some of the content. <aside> serves as a sidebar to the main content.
The <footer> element
The <footer> element is usually found at the bottom of an HTML document. <footer> contains legal information, the author’s details, and links to relevant information pertaining to the website.
Browser compatibility
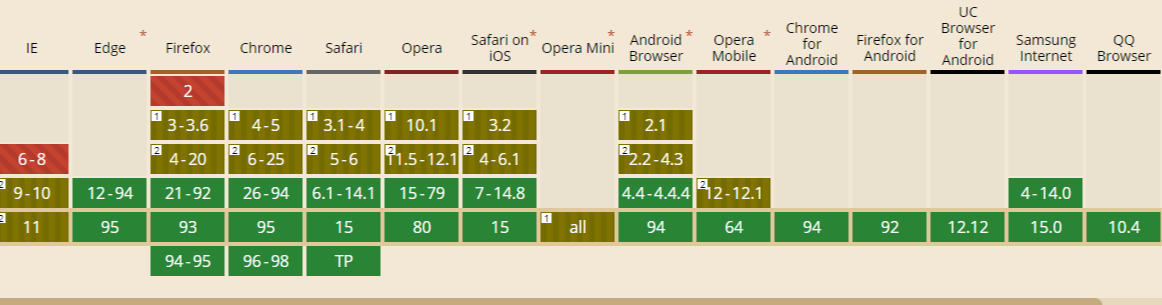
The image below shows the browser compatibility statistics of the semantic HTML5 elements.
HTML5 semantics is supported across the newer versions of most browsers.
Conclusion
HTML5 semantics is a modern approach for laying out web pages, although non-semantic markup can be found across older websites. HTML5 semantics provides a consistent way to structure web content and makes it easy for computers and developers to read web content. It is compatible with most modern browsers.
 Source:
Source: