How to use the node package manager?
If we decide to migrate to JavaScript as a backend for your next application, our only option is to use Node.js. The software we build always relies on other software, and the node package manager (npm) lets us easily manage dependencies within our applications. We can compare npm to the composer in PHP.
The purpose of this shot is to learn you how to use npm effectively.
Prerequisites: We should have
Node.jsinstalled on your system.
npm in a nutshell
npm is a dependencies’ manager’s tool. More precisely, npm is a Node.js by default. So, if we have Node.js installed on your system, we also have npm.
Note: To check if we have
Node.jsinstalled on your system, we can typenode --versionin a shell or terminal window.
To work with npm, we need to prepare our workspace by doing the following.
- Create a project directory:
mkdir myProject - Make it a
Node.jsproject:npm init
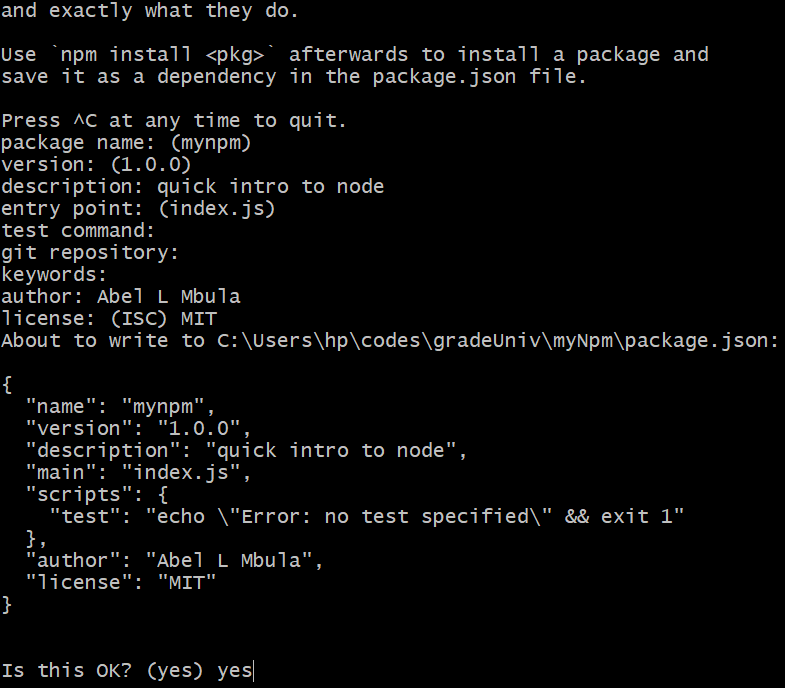
The second command will prompt us with some questions we need to answer.
After that, we type yes and hit the “Enter” button. npm will then create a package.json file with all the information.
Note: If you want to use the default answers from
npm init, you can typenpm init -y.
Basic npm commands
We can use the following basic commands in a terminal:
npm -vornpm — version: It gets thenpmversionnpm install -g npm: It updatesnpmto the latest releasenpm i <packageName>ornpm install <packageName>: It installs a packagenpm uninstall <packageName>: It uninstalls packagepackageNamenpm outdated: It checks for an updated version of a packagenpm update <packageName>: It updatespackageNamenpm search <name>: It searches for a packagenpm cache clean — force: It cleans the cachenpm audit: It audits packages for known security vulnerabilitiesnpm ls: It shows the installed packagesnpm help: It gets help
Install packages
Now, we will install dependencies in our project.
First, we should have a clean and ready Node.js workspace.
The package we want to install is express, a Node.js framework.
npm i express
npm fetch express from npmjs.com, which is the default registry it uses. A registry is a public database of JavaScript software.
After the package downloads, npm places it in a special directory called node_modules. The reference of the module is written in the package.js file under the dependencies section. We can view the package by entering ls in the terminal.
node_modules:is the default directory used byNode.jsuses to find any package it needs. We can think of this folder as a local store for your downloaded packages.
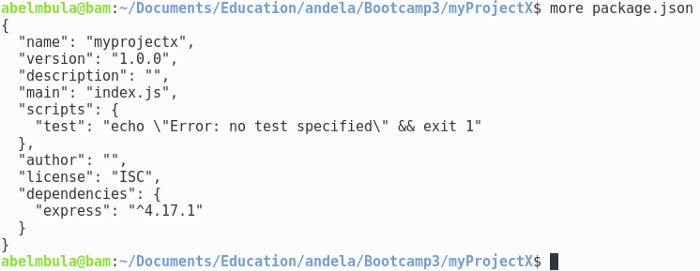
Our recently installed express module is shown below:
The package.json and package-lock.json files
The reference for the express package was written in the package.json file.
This is the case for any package we install. This is important because it makes it easy for us to start our project in a new instance be it a computer or another directory.
Additionally, we’ll need to use .gitignore on the node_modules folder when working with git. This is because it is so big and does not belong to us or our project codebase. The only way to reinstall all packages used in the project is via package.json.
We delete node_modules and run npm install. This will create the directory again, and install all referenced modules in package.json.
The package-lock.json file helps lock the same version used for our project dependencies. It guarantees that anyone installing our project dependencies will have the same versions as ours.
Summary
npm is a JavaScript package manager for Node.js. To make a Node.js project, we have to use npm init.
We use npm install <moduleName> is used to install packages. All installed packages are stored in the node_modules directory, and referenced in package.json under the dependencies section. Lastly, package-lock.json locks the version of the dependencies we use in our project.
Happy coding!