How to use freopen() in C++
freopen() is a built-in function defined in the <cstdio> header that redirects an existing FILE pointer to another stream. This function is used in file reading and writing.
The function works in the following way:
- The function closes the file associated with the stream, ignoring any errors.
- If filename is not NULL, it will open a file with the name specified in the filename argument in the mode specified in the mode argument. Else, if filename is NULL, it attempts to open a file that was previously associated with the stream.
- The new file is associated with the file stream specified in the stream argument.
This is different from fopen(), which only opens a file in the specified access mode; whereas, freopen() is used to redirect standard input, output, and error to a specified file.
Prototype
FILE* freopen(const char* filename, const char* mode, FILE* stream);
Parameters:
- filename: Name of the file to be opened.
- mode: Access mode of the file to be opened.
- stream: The file stream that filename it is associated with. Examples include stdin, stdout, and stderr.
There are six access modes that a file can be opened with:
| Access mode | Meaning | If filename is valid | If filename is NULL |
|---|---|---|---|
| “r” | Read: open file to read only | Reads file from start | Undefined Behavior |
| “w” | Write: open file to write only | Deletes all data in file | Creates new file |
| “a” | Append: write at the end of file | Starts writing from end of file; preserves previous data | Creates new file |
| “r+” | Opens file to read and write both | Reads file from start | Undefined Behavior |
| “w+” | Opens file to read and write both | Deletes all data in file | Creates new file |
| “a+” | Opens file to read and write in append mode | Starts writing from end of file; preserves previous data | Creates new file |
Return value
If successful, the function will return stream and clear any errors associated with the stream. Else, NULL is returned.
Syntax with example code
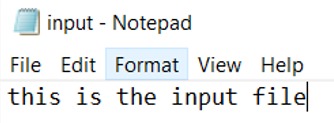
Input file
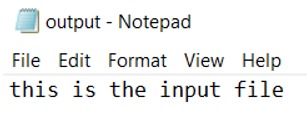
Start with an existing text file (.txt) named “input” with any string. For example, “this is the input file.”
Code
#include <cstdio>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){// associates standard input with input.txtfreopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);// associates standard output with output.txt// (this will create a new file called output.txt if none exists)freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);string x;// reads the input.txt file and stores in string xgetline(cin, x);// prints string x in output.txt filecout << x;return 0;}