How to create a delete view function using Django
In this shot, we talk about how to create a delete view function using Django. It is used to delete a particular instance of a table from the database.
Installation
Let’s start with installation:
Note:
pipis a package manager for Python packages.
Step 1:
pip install pipenv
pipenv shell
pipenv install django
Step 2:
django-admin startproject crud ./
python manage.py startapp codebase
Step 3:
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserver
Next, we configure settings.py
Configuring settings.py
settings.py helps register your app and packages that are being installed and write rules.
Add the following code to the settings.py file.
INSTALLED_APPS = ['django.contrib.admin','django.contrib.auth','django.contrib.contenttypes','django.contrib.sessions','django.contrib.messages','django.contrib.staticfiles','codebase']
Next, go to models.py in the codebase app folder.
Configuring models.py
This file is responsible for creating the model for the database.
from django.db import modelsfrom django.urls import reverseclass CRUD(models.Model):name = models.CharField(max_length=30)age = models.IntegerField()level = models.CharField(max_length=30)date = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)#display the data with namedef __str__(self):return self.name
Configuring admin.py
In this file, we register the model we’ve created by importing it. By doing so, we can see it when logged in as admin.
from django.contrib import adminfrom .models import CRUDadmin.site.register(CRUD)
Create a file and name it forms.py
Configuring forms.py
The forms file is responsible for creating Django forms. Django forms are similar to HTML forms, except they are dynamic.
from django import formsfrom .models import CRUDclass CRUDFORM(forms.ModelForm):name = forms.CharField(widget=forms.TextInput(attrs={"class": "form-control","placeholder": "name"}))age= forms.CharField(widget=forms.TextInput(attrs={'type': "number","class": "form-control","placeholder": "age"}))level = forms.CharField(widget=forms.TextInput(attrs={"class": "form-control","placeholder": "level"}))class Meta:model = CRUDfields = ['name', 'age','level']
Configuring views.py
This file is used to create functions or classes that visualize how a route will operate.
from django.shortcuts import redirect, render, get_object_or_404from .models import CRUDfrom .forms import CRUDFORMdef home(request):queryset = CRUD.objects.all().order_by('-date')context = {'queryset': queryset}return render(request, 'app/base.html', context)def create(request):form = CRUDFORM(request.POST or None)if request.method == "POST":if form.is_valid():form.save()return redirect ('home')context = {"form":form}return render(request, 'app/createform.html', context)def delete(request, id):data = get_object_or_404(CRUD, id=id)data.delete()return redirect('home')
In the codebase app, create a folder and name it templates. Inside the templates folder, create another folder and name it app. Then, inside the app folder, create base.html, delete.html and createform.html files.
Configuring base.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Crud</title><link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.0-beta1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-giJF6kkoqNQ00vy+HMDP7azOuL0xtbfIcaT9wjKHr8RbDVddVHyTfAAsrekwKmP1" crossorigin="anonymous"></head><body><div class="container mt-3"><a href="{% url 'create'%}" >link to create a form</a><hr>{% for data in queryset %}<div class="list-group mb-3"><a href="#" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">Name: {{data.name}}</a><a href="#" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">Age: {{data.age}}</a><a href="#" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">Level: {{data.level}}</a><a href="{% url 'delete' data.id %}">delete</a></div>{% endfor %}<hr></div></body></html>
Configuring createform.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Crud</title><link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.0-beta1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-giJF6kkoqNQ00vy+HMDP7azOuL0xtbfIcaT9wjKHr8RbDVddVHyTfAAsrekwKmP1" crossorigin="anonymous"></head><body><div class="container mt-5"><form method="POST" action="">{% csrf_token %}<div class="form-group mb-3">{{form.name}}{{form.name.errors}}</div><div class="form-group mb-3">{{form.age}}{{form.age.errors}}</div><div class="form-group mb-3">{{form.level}}{{form.level.errors}}</div><input type="submit" class="btn btn-outline-success" ></form></div></body>
In the crud folder, go to the urls.py file.
Configuring crud/urls.py
from django.contrib import adminfrom django.urls import path, includeurlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),# including the codebase urls.py filepath('', include('codebase.urls'))]
Then in the codebase folder, create a file and name it urls.py.
This file is responsible for creating different routes.
Configuring codebase/urls.py
from django.urls import pathfrom .view import home, create, deleteurlpatterns = [path('',home, name="home" ),path('create/', create, name="create"),path('delete/<str:id>/', delete, name="delete"),]
Testing
Run the following commands:
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
In case you want to create a super-user, run the following command:
python manage.py createsuperuser
After this, run:
python manage.py runserver
Then go to http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin and login in order to access the admin panel or http://127.0.0.1:8000/ to access the homepage
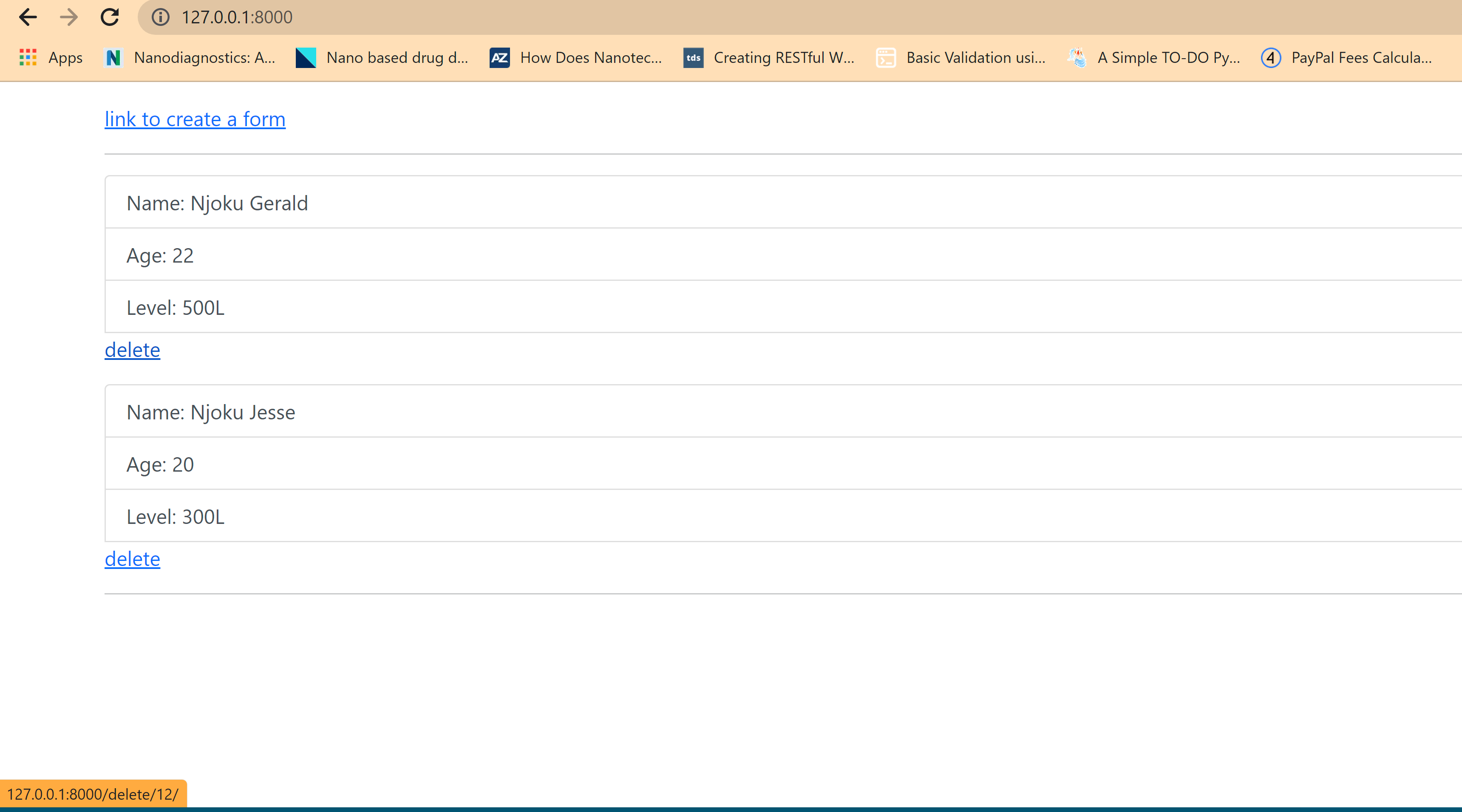
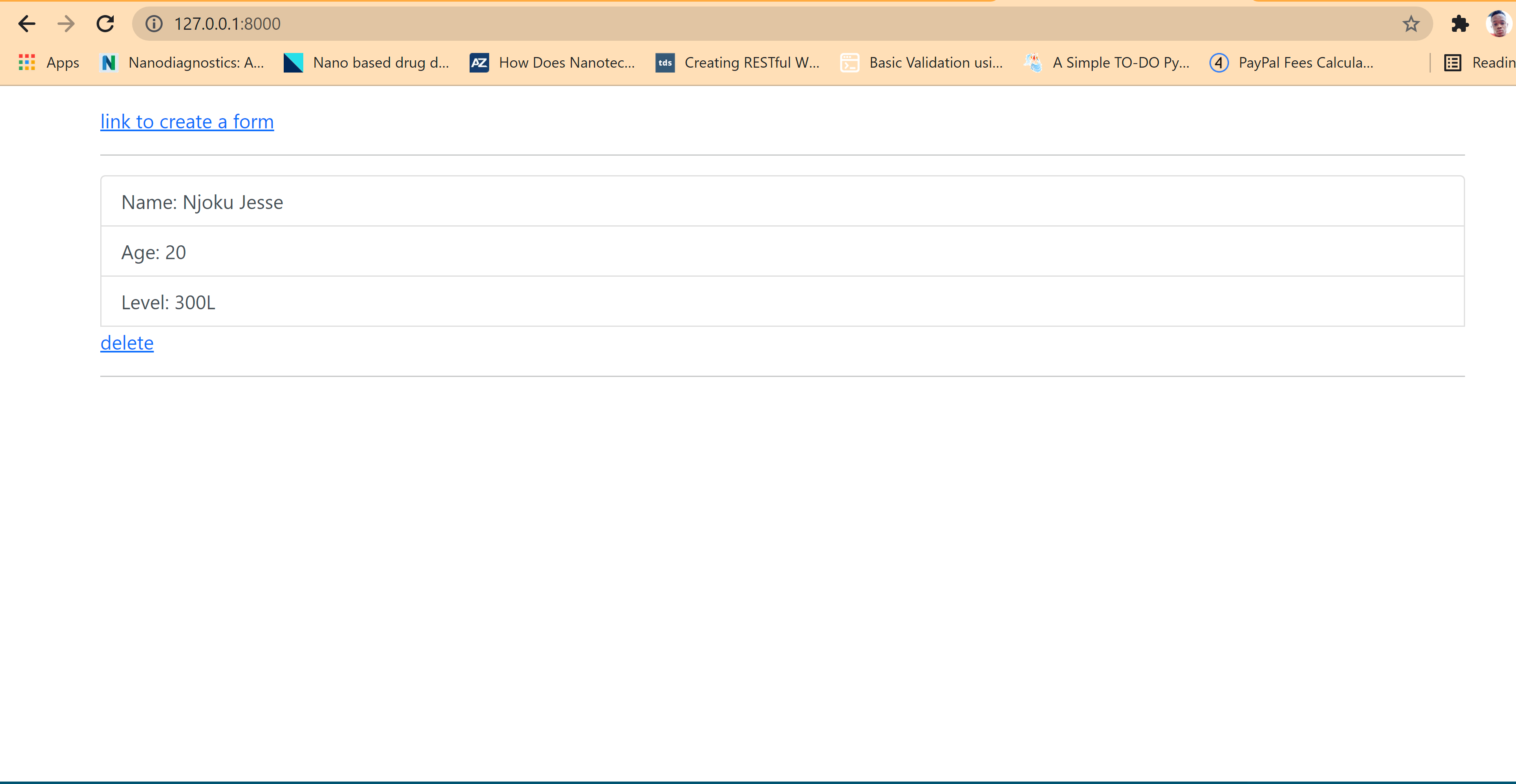
Output
The following is a sample output:
before deleting data:
after deleting data: