Handling incoming dynamic links
This is part 2 of the series React Native Deep Linking Simplified. In part 1, we learned how to add deep links. In this article, our goal is to learn how to handle incoming links like a pro. We will also see how to route the user to a particular screen based on the incoming link.
The term deep link is used for the
httpsscheme and Dynamic Link is used for theappscheme. We can use both to navigate our user so that we don’t get confused between these two terms.
Let’s get started.
Project setup
We will use the react-native-firebase module to configure Dynamic Links in our React Native Project. It involves 4 simple steps:
Steps involved
- Create a React Native project
- Create an application on the Firebase Console
- Add
react-native-firebase - Add the Firebase Dynamic Links module
1. Create a React Native project
Follow the steps in part 1 and add the deep link as described. We will be adding firebase-invites support via the same Dynamic/Deep link we created earlier.
2. Create an application on the Firebase Console
Let’s create an application on the Firebase Console to use the Firebase SDK. Create an
- Create a project by clicking on Add Project.
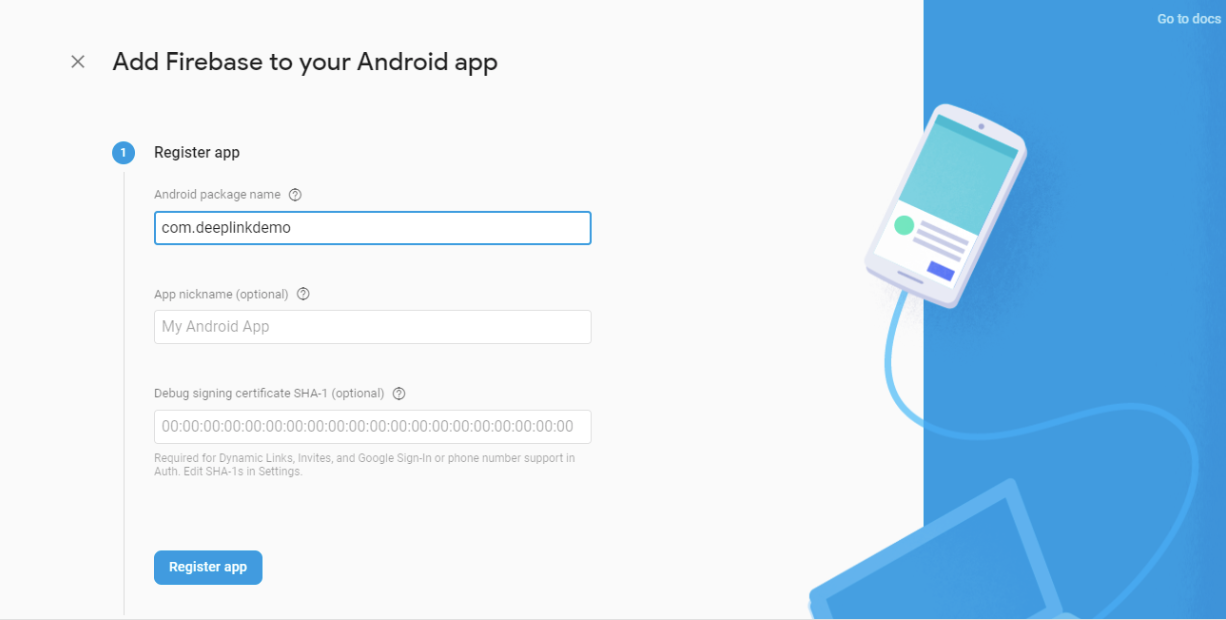
- Follow the steps to add Android/iOS app. Make sure the project name in the Register app section matches with your React Native project (
com.deeplinkdemoin our case).
- Download
google-services.jsonand paste it inside*/deeplinkdemo/android/app/*. Make sure the location is correct.
- Add libraries as instructed and Sync Project. It will look something like this:
dependencies {classpath("com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.4.1")classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.0' //Add this line}
dependendies {//...implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-core:17.0.1' // Add this line}//Add to the bottom of the fileapply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'
Please use the latest firebase dependency available. You can add it from Android Studio also by going to:
File -> Project Structure -> Dependencies
3. Add react-native-firebase
Go to your project’s root directory and run this command:
npm install react-native-firebase --save
(Optional) Link the module if your react-native version is less than .
react-native link react-native-firebase
React Native version (>0.60) supports autolinking.
Follow the Manual Linking guide below if you’re having any issues linking react-native-firebase or if you’re using an earlier version of React Native.
Manual Linking for React Native (<0.60)
Check out the official
Android
- Add
react-native-firebaseto the App-levelbuild.gradle:
dependencies {//...implementation project(':react-native-firebase') //Add this line}
- Edit
settings.gradle:
//Add these linesinclude ':react-native-firebase'project(':react-native-firebase').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-firebase/android')
- Edit
MainApplication.java:
...import io.invertase.firebase.RNFirebasePackage; // import this@Overrideprotected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(new MainReactPackage(),new RNFirebasePackage(), // Add this line);}
- Sync Project and we are good to go.
4. Add the Firebase Dynamic Links module
We have to include other modules as the RNFirebasePackage we imported earlier only provides the core features.
If you go to the Firebase Invites Docs, you will see a warning.
Firebase Invites is deprecated. You can create cross-platform invitation links that survive app installation using Firebase Dynamic Links. Please see the Migration Guide for more details.
It means that we will eventually be using the
- Add the dependency to
android/app/build.gradlefile:
dependencies {// ...implementation "com.google.firebase:firebase-dynamic-links:19.0.0" //Add this lineimplementation "com.google.firebase:firebase-invites:17.0.0" //Add this line}
- Edit
MainApplication.java:
import ...//import this packageimport io.invertase.firebase.links.RNFirebaseLinksPackage;@Overrideprotected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(new MainReactPackage(),new RNFirebasePackage(),new RNFirebaseLinksPackage() // Add this line);}
- For
react-native@0.60and above:
@Overrideprotected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {@SuppressWarnings("UnnecessaryLocalVariable")List<ReactPackage> packages = new PackageList(this).getPackages();// Packages that cannot be autolinked yet can be added manually here, for// example:// packages.add(new MyReactNativePackage());packages.add(new RNFirebaseLinksPackage());// Add this linereturn packages;}
- Sync Project and we are done.
If you’re running into some dependency issues then migrate to AndroidX. Check How to solve dependency issues at the end of part 3.
See the
for updated method. official docs https://firebase.google.com/docs
Free Resources
- undefined by undefined